Chiranjeet Rege, Director, SILICA has been with the organisation for 10yrs in an entrepreneurial role. Before joining SILICA, he was Audit Manager with Deloitte LLP London for 3 years and the previous 3 years as Audit Executive with KPMG Mumbai and KPMG London. He aims to deliver exceptional quality education and guidance to SILICA students by building teams, systems and technology which will consistently deliver the SILICA promise of exceptional quality.
The Problems We Face:
The human race is approached by many problems and challenges on a daily basis. These problems occur at different levels- personal, societal, organizational, national and global. Some problems are simple and some are more complex and ambiguous. In today’s world, we are affected by problems in all spheres such as climate change, malnutrition, poverty, technological advancement, terrorism, recession, unemployment, business, profession, education, medical breakthroughs and so on. The great Albert Einstein said, “We can’t solve problems by using the same kind of thinking we used when we created them”. Design Thinking in a unique way these complex, open ended problems.
What is Design Thinking:
A strategy to identify and resolving human problems is design thinking. It can be useful in addressing difficult problems that are complicated and unknown. It involves comprehending human needs, framing the issue from a human perspective, coming up with original ideas, narrowing down viable solutions to the most practical and workable ones, prototyping, and testing the chosen solution. Design Thinking’s unique approach can also lead to new innovations in products, services, processes, environments, and other human experiences.
Problem-Solving Through Design Thinking:
The number of steps in the Design Thinking process can range from 3 to 7. A five-stage process is suggested by the Hassno Plattner Institute of Design (Stanford D-School). These stages are not sequential; they frequently run parallel, out of sequence, and iteratively.
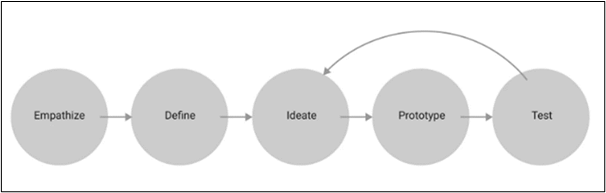
- Empathize: knowing the user’s issues, requirements, and preferences in-depth By doing this, the user is kept at the core of the process. Important skills needed during this phase are empathy, listening, and communicating. Engage & Interact, User Research, Interviews, Surveys, Observation, etc. are some of the methods used.
- Define: Here, you define the issue in a manner that is human-centered. To create a “Problem Statement,” you will compile and evaluate all you have learned during the Empathize stage. The “Problem Statement” should be written from the user’s perspective. Critical Thinking and Communication Skills are needed at this stage. For example, you should not define the problem from a business standpoint, such as “We need to expand the number of designers we train by 50%.” You should phrase the problem from the user’s perspective: “To be successful in life, young Indians must pursue Creative Careers if they have the proper Aptitude & Interest.”
- Ideate: You are prepared to come up with ideas at this point. To the problem at hand, you will come up with innovative and creative ideas. Identify different perspectives on the problem and generate as many ideas as you can. For this stage, you’ll use strategies such as body storming, mind mapping, role-playing, brainstorming, four-step sketching, and others. This phase requires for creativity, imagination, and innovative abilities.
- Prototype: At this stage, you narrow down the top 3-4 best solutions from the various ideas you’ve evaluated. Here, you create scaled-down and reduced versions of the top 3-4 ideas. You turn the concepts into a prototype, test it, and challenge the solution. The answers are put into practise in the prototype and are then either approved, rejected, or revised based on the feedback from test users until you find the ideal solution. Critical Thinking and Communication skills are necessary at this stage.
- Test: During this stage, you will carefully test the entire product utilising the best solution selected during the prototyping stage. Even though this is the last step, it can alternate between the earlier stages because it is iterative. Based on the knowledge and understanding gained in Stages 1 through 4, this stage is frequently iterative. Understanding the solutions and its users as deeply as possible is the ultimate goal of this stage.
Important Principles of Design Thinking for Problem Solving:
- Is Human Centric: both the problem and the eventual solution is framed from the human centered approach. You focus on the people or community, understand their desires, needs, problems and try to solve them.
- Different from Scientific Problem Solving: Scientists often solve problems through analysis, whereas design thinking requires analysis, ideation, imagination, empathy and Analyses.
- Involves Divergent & Convergent Thinking: Design Thinkers will evolve as many possible solutions as they can think of (divergent thinking) and then they will apply the scientific & logical side (convergent thinking) to narrow them down to the most suitable option.
- Is Experimental & Iterative: Design thinking process is not linear advancing through the different stages. Rather it is an iterative process where you can loop back to any stage to enhance the outcome or solution. Changing based on feedback and experiments is essential to the process.
- Is Collaborative: Design Thinking process cannot happen in isolation or in a laboratory. It requires inputs and active participation from all stakeholders e.g. in a manufacturing problem, you will need inputs from future customers, engineers, management, labourers and so on.
In today’s rapidly changing world, Design Thinking applies to all great thinkers and inventors in science, engineering, medicine, business, literature, art, and so on. The majority of well-known companies, like Bank of America, Nike, Samsung, Apple, Google, IBM, Pepsi, Netflix, and Airbnb, have embraced the Design Thinking methodology to address their business problems and innovate. Design thinking is beneficial irrespective of your role or industry. Design thinking can help you build innovative solutions based on the demands of your stakeholders, whether you are in business, government, education, or non-profit. Therefore, in order to solve every day professional and personal problems, all professionals must understand and apply Design Thinking.
Importance of 4Cs in Higher Education:
The world today is unstable and undergoing rapid change. To respond to these challenges and succeed, every student in a professional course needs to be adaptable and skilled. Higher order talents like Creativity, Critical Thinking, Collaboration, and Communication (commonly referred to as the 4C skills) are frequently sought after in 21st century workplaces. Additionally, companies are looking for soft skills like empathy, flexibility, decision-making, and problem-solving. The recently released National Education Policy, NEP 2020 by the Government of India also espouses these same concepts for skill development. Design Thinking enables aspiring students and professionals to develop these higher order and life skills.
Amongst all the higher order skills, Creativity is the most neglected in the Indian education system. Students are encouraged to focus on Science, Technology, Engineering and Medicine, often called STEM subjects. Creativity is defined as the ability to produce original, unique and new ideas, methods or things, to help solve problems, innovate, communicate and live better. Creativity helps to generate or recognize ideas, connections, alternatives, or possibilities. It is the ability to transcend the traditional ways of thinking and imagining new and original ideas. Creativity is at the essence of any innovation or transformation. As per World Economic Forum, Creativity is an essential skill for the 21st Century Professional.
Creativity is important in education for the following reasons:
- It builds ability in students to understand complex information and situations
- It helps in developing collaboration skills and empathy
- It allows students to express themselves freely
- It encourages students to be lifelong learners
- It promotes risk taking and innovation
- It promotes thinking outside the box and solving problems
One of the myths about Creativity is that it cannot be learned. Multiple studies and research have shown that creativity is as much as skill that can be acquired and fostered as it is inborn. The NEP 2020 has renewed focus on bringing creativity to Indian classrooms, which bodes well for Indian youth.




